Choosing the right wire rope fitting is crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of any lifting or rigging operation. The selection process involves understanding various factors, from the type of wire rope used to the specific demands of the application. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the essential considerations, helping you make informed decisions that enhance the reliability and longevity of your equipment.
Understanding Wire Rope and Its Applications
The Basics of Wire Rope Construction
Wire rope is a complex assembly of wires, strands, and a core, each contributing to its overall strength and flexibility. The wires are twisted together to form strands, which are then laid helically around the core. The core provides support to the strands and maintains their position during bending. Understanding this basic construction is the first step in appreciating the importance of proper wire rope termination.
Different materials are used in the construction of wire rope, including carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel. The choice of material depends on the application’s requirements, considering factors such as load, environment, and expected lifespan. For instance, in marine environments, stainless steel is often preferred for its superior corrosion resistance. We’ve seen firsthand, especially with our clients working on offshore platforms near Dubai, the costly consequences of neglecting material selection. The wrong choice can lead to premature failure and significant downtime.
[IMAGE: Cross-sectional diagram of a typical wire rope, showing the wires, strands, and core.]
Different Types of Wire Rope
Wire ropes are classified based on their construction, lay type, and core type. Common constructions include:
- Regular Lay: The wires in the strands and the strands in the rope are laid in opposite directions. This type offers good resistance to crushing and abrasion.
- Lang Lay: The wires in the strands and the strands in the rope are laid in the same direction. This provides greater flexibility and wear resistance but is more prone to untwisting.
- Alternate Lay: A combination of regular and lang lay, offering a balance of properties.
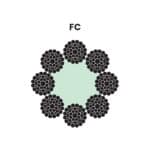
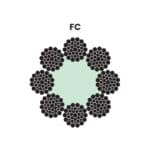
The core of the wire rope can be made of fiber (FC), independent wire rope (IWRC), or wire strand (WSC). Fiber cores provide greater flexibility, while wire cores offer higher strength and resistance to crushing. The type of wire rope sling and the appropriate cable hardware greatly depend on these factors.
Knowing these classifications will help you narrow down the type of wire rope best suited for your specific application. For example, if you’re working with heavy loads and need maximum strength, a wire rope with an IWRC core and a regular lay construction might be the best option.
Common Applications of Wire Rope
Wire rope is used in a wide range of applications across various industries. Some common examples include:
- Construction: Cranes, hoists, and elevators rely on wire rope for lifting and moving heavy materials.
- Marine: Winches, mooring lines, and towing cables in ships and offshore platforms use wire rope extensively.
- Mining: Hoists and draglines in mining operations depend on wire rope for extracting materials.
- Oil and Gas: Drilling rigs and offshore platforms utilize wire rope for various lifting and tensioning applications.
- Manufacturing: Overhead cranes and lifting systems in factories use wire rope for material handling.
Each application places different demands on the wire rope and its fittings. For instance, a crane lifting heavy loads on a construction site requires high-strength wire rope and fittings that can withstand significant stress, while a mooring line on a ship needs excellent corrosion resistance to withstand the harsh marine environment. Choosing the right wire rope fitting is therefore crucial to ensuring safe and effective operation in these diverse scenarios.
Identifying Your Lifting Requirements
Determining the Load Weight
Accurately determining the load weight is the first and most critical step in selecting the appropriate wire rope fitting. Underestimating the load can lead to catastrophic failure, while overestimating can result in unnecessary costs and reduced efficiency. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for the weight of the load you are lifting.
It’s essential to consider not only the weight of the primary load but also any additional weight from attachments, such as slings, shackles, and other rigging hardware. Using calibrated scales or load cells to verify the weight is a best practice, especially for critical lifts. Safe and Secure Trading Company (SSTC) emphasizes this step during our training sessions, as we’ve observed that many accidents occur due to inaccurate weight assessments.
[IMAGE: A worker using a calibrated scale to weigh a load before lifting.]
Calculating Dynamic Loads and Safety Factors
In addition to the static load weight, you must also consider dynamic loads, which are forces generated by motion or sudden impacts. Dynamic loads can significantly increase the stress on the wire rope and its fittings. Examples of dynamic loads include:
- Shock Loading: Sudden impact caused by abrupt starts or stops.
- Acceleration and Deceleration: Forces generated during lifting or lowering operations.
- Wind Loads: Forces exerted by wind on the load and rigging.
To account for dynamic loads, a safety factor is applied to the Working Load Limit (WLL) of the wire rope and its fittings. The safety factor is a multiplier that ensures the actual load never exceeds the safe working capacity. The appropriate safety factor depends on the application, industry standards, and regulatory requirements. We generally recommend a safety factor of at least 5:1 for critical lifting applications, but this can vary depending on specific circumstances.
The formula to calculate the required WLL is:
Required WLL = (Maximum Load x Dynamic Load Factor) x Safety Factor
Properly calculating dynamic loads and applying appropriate safety factors are essential for preventing failures and ensuring lifting safety.
Evaluating Environmental Conditions
Environmental conditions can significantly affect the performance and lifespan of wire rope and its fittings. Factors to consider include:
- Temperature: Extreme temperatures can alter the strength and ductility of materials.
- Corrosion: Exposure to moisture, chemicals, or salt can accelerate corrosion and weaken the wire rope and fittings.
- Abrasion: Contact with abrasive surfaces can cause wear and reduce the diameter of the wire rope.
- UV Exposure: Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation can degrade certain materials, such as fiber cores.
For example, in offshore environments, stainless steel or specially coated fittings are necessary to withstand the corrosive effects of saltwater. Similarly, in high-temperature environments, alloy steel fittings with high heat resistance are preferred. Understanding the environmental conditions and selecting materials and coatings accordingly will help ensure the long-term reliability and safety of your lifting operations. Our team in Dubai frequently advises clients on these considerations, helping them choose the most suitable cable hardware for their specific operating environment.
Types of Wire Rope Fittings: A Comprehensive Overview
Swage Fittings: Pros, Cons, and Application Scenarios
Swage fittings are a popular choice for creating strong and reliable terminations on wire rope. These fittings are mechanically deformed onto the wire rope using a swaging machine, creating a permanent connection.
Pros:
- High Strength: Swage fittings can achieve a high percentage of the wire rope’s tensile strength.
- Clean Appearance: They provide a streamlined and professional look.
- Permanent Connection: Once swaged, the connection is highly resistant to loosening.
Cons:
- Requires Specialized Equipment: Swaging requires a swaging machine and skilled operators.
- Non-Removable: Once swaged, the fitting cannot be easily removed or reused.
- Susceptible to Corrosion: If not properly protected, swage fittings can be susceptible to corrosion, especially in harsh environments.
Application Scenarios:
- Architectural cable railings
- Aircraft control cables
- Suspension bridges
- Marine rigging
When using swage fittings, it’s crucial to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper swaging techniques. This includes using the correct die size, applying the appropriate pressure, and inspecting the swaged connection for any defects.
[IMAGE: A close-up of a swaged wire rope fitting, showing the deformation of the fitting around the wire rope.]
Clip Fittings: Installation, Limitations, and Best Practices
Clip fittings, also known as wire rope clips or U-bolt clips, are a simple and versatile method for creating terminations or loops in wire rope. They consist of a U-bolt, a saddle, and nuts that clamp the wire rope together.
Pros:
- Easy Installation: Clip fittings can be installed with simple hand tools.
- Reusability: They can be removed and reused, making them suitable for temporary applications.
- Versatility: Clip fittings can be used in a variety of applications.
Cons:
- Lower Strength: Clip fittings typically have a lower holding strength compared to swage fittings.
- Potential for Slippage: If not properly installed and tightened, clip fittings can slip, leading to failure.
- Damage to Wire Rope: Overtightening can crush the wire rope and reduce its strength.
Installation Best Practices:
1. Orientation: The saddle of the clip should always be placed on the live or load-bearing side of the wire rope.
2. Spacing: Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the number of clips and their spacing.
3. Tightening: Tighten the nuts to the specified torque using a torque wrench.
4. Re-Tightening: Re-tighten the nuts after the initial load is applied, as the wire rope may stretch and settle.
While clip fittings offer convenience and flexibility, it’s essential to understand their limitations and follow proper installation procedures to ensure safe and reliable performance.
Wedge Sockets: When to Use Them and How They Work
Wedge sockets provide a strong and reliable method for terminating wire rope, particularly in applications where frequent adjustments or replacements are required. They consist of a basket, a wedge, and a pin that secures the wire rope in place.
When to Use Wedge Sockets:
- Crane Boom Hoists: Where the wire rope needs to be frequently adjusted.
- Draglines: In mining operations where the wire rope is subjected to heavy loads and abrasion.
- Suspension Bridges: For anchoring the main cables.
How They Work:
The wire rope is inserted into the basket, looped around the wedge, and then secured by the pin. As the load is applied, the wedge tightens against the wire rope, creating a strong grip.
Advantages of Wedge Sockets:
- Easy Installation and Adjustment: They can be easily installed and adjusted in the field.
- High Holding Strength: Wedge sockets can achieve a high percentage of the wire rope’s tensile strength.
- Visual Inspection: The connection can be visually inspected for proper seating and wear.
When using wedge sockets, it’s crucial to ensure the wire rope is properly seated in the basket and that the wedge is fully engaged. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for wear or damage to the socket and wedge.
[IMAGE: Exploded view of a wedge socket, showing the basket, wedge, and pin.]
Thimble Eyes: Protecting the Wire Rope and Enhancing Durability
A thimble eye is a teardrop-shaped fitting inserted into the loop of a wire rope to protect it from wear and distortion. It provides a smooth, curved surface for the wire rope to bear against, preventing kinking and abrasion.
Benefits of Using Thimble Eyes:
- Increased Wire Rope Lifespan: By reducing wear and distortion, thimble eyes can significantly extend the lifespan of the wire rope.
- Improved Load Distribution: They distribute the load more evenly across the wire rope, reducing stress concentrations.
- Enhanced Safety: By preventing kinking and abrasion, thimble eyes improve the overall safety of the lifting operation.
Applications:
- Wire Rope Slings: Thimble eyes are commonly used in wire rope slings to protect the loops from wear.
- Mooring Lines: In marine applications, thimble eyes are used to protect the wire rope from abrasion against shackles and other hardware.
- Guy Wires: For anchoring towers and antennas.
When selecting a thimble eye, ensure it is the correct size for the wire rope and that it is made of a compatible material. Regular inspections should be conducted to check for wear or damage to the thimble eye.
Other Fitting Types: Shackles, Turnbuckles, and Eye Bolts
In addition to the fittings discussed above, several other types of fittings are commonly used in conjunction with wire rope.
- Shackles: U-shaped or bow-shaped fittings used to connect different components of a lifting system. They are available in various sizes and load capacities.
- Turnbuckles: Devices used to adjust the tension in wire rope assemblies. They consist of a body with threaded ends that accept eye bolts or hooks.
- Eye Bolts: Bolts with a looped head used for attaching wire rope or other hardware to a structure.
These fittings play a crucial role in creating complete and functional lifting systems. When selecting these fittings, it’s essential to consider their load capacity, material, and compatibility with the wire rope and other hardware.
Load Capacity and Safety Considerations for Each Fitting Type
Understanding Working Load Limit (WLL)
The Working Load Limit (WLL) is the maximum load that a wire rope fitting is designed to safely carry. It is typically marked on the fitting and should never be exceeded. The WLL is determined by dividing the minimum breaking strength (MBS) by a safety factor.
Understanding the WLL of each fitting is critical for ensuring safe lifting operations. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and markings to determine the WLL. Remember that the WLL applies only when the fitting is used in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
[IMAGE: A close-up of a wire rope fitting, showing the WLL marking.]
Breaking Strength vs. WLL: The Importance of Safety Factors
The breaking strength, also known as the minimum breaking strength (MBS) or ultimate tensile strength (UTS), is the force required to cause a fitting to fail. The WLL is always lower than the breaking strength to provide a margin of safety.
The safety factor is the ratio of the breaking strength to the WLL. It is intended to account for uncertainties in the load, environmental conditions, and material properties. Common safety factors for wire rope fittings range from 4:1 to 5:1, but higher safety factors may be required for critical applications.
The formula is:
Safety Factor = Breaking Strength / WLL
Using appropriate safety factors is essential for preventing failures and ensuring the safety of lifting operations.
Derating Factors for Different Applications
In some applications, the WLL of a wire rope fitting may need to be reduced or “derated” to account for specific conditions. Derating factors may be applied for:
- Dynamic Loading: As discussed earlier, dynamic loads can significantly increase the stress on fittings.
- Angle Loading: When fittings are used at an angle, their effective WLL is reduced.
- Elevated Temperatures: High temperatures can reduce the strength of materials.
- Corrosive Environments: Corrosion can weaken fittings over time.
Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications and industry standards to determine the appropriate derating factors for your application. Neglecting these factors can lead to overloading and failure.
Avoiding Overloading and Ensuring Safe Operation
Overloading is a leading cause of wire rope fitting failure. To avoid overloading:
- Accurately Determine the Load Weight: Use calibrated scales or load cells to verify the weight of the load.
- Consider Dynamic Loads: Account for dynamic loads and apply appropriate safety factors.
- Know the WLL of Each Fitting: Refer to the manufacturer’s specifications and markings.
- Use a Load Monitoring System: Consider using a load monitoring system to track the load on the wire rope and fittings in real-time.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections to check for wear, damage, and corrosion.
By following these guidelines, you can minimize the risk of overloading and ensure safe operation.
Material Selection for Wire Rope Fittings
Carbon Steel: Properties, Advantages, and Disadvantages
Carbon steel is a common material for wire rope fittings due to its high strength and relatively low cost.
Properties:
- High Tensile Strength
- Good Ductility
- Weldable
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective
- Widely Available
- Suitable for General-Purpose Applications
Disadvantages:
- Susceptible to Corrosion
- Lower Strength at Elevated Temperatures
- May Require Protective Coatings
Carbon steel fittings are often used in applications where corrosion is not a significant concern or where protective coatings can be applied. However, in harsh environments, stainless steel or alloy steel may be a better choice.
Stainless Steel: Corrosion Resistance and High-Strength Applications
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance, making it ideal for marine, chemical, and other harsh environments.
Properties:
- High Corrosion Resistance
- Good Tensile Strength
- Hygienic
Advantages:
- Excellent Resistance to Corrosion
- Suitable for Marine and Chemical Environments
- Long Lifespan
Disadvantages:
- Higher Cost
- Lower Strength Compared to Alloy Steel
- May be Susceptible to Chloride-Induced Stress Corrosion Cracking
Stainless steel fittings are commonly used in applications where corrosion is a major concern, such as offshore platforms, ships, and food processing plants. Our experience at SSTC suggests that investing in stainless steel fittings can significantly reduce maintenance costs and extend the lifespan of equipment in corrosive environments.
Alloy Steel: High-Performance Options for Demanding Environments
Alloy steel offers the highest strength and toughness of the three materials, making it suitable for demanding environments and heavy-duty applications.
Properties:
- Very High Tensile Strength
- Excellent Toughness
- Good Fatigue Resistance
Advantages:
- Highest Strength-to-Weight Ratio
- Suitable for Heavy-Duty Applications
- Good Resistance to Fatigue
Disadvantages:
- Highest Cost
- May Require Heat Treatment
- Susceptible to Corrosion if Not Properly Protected
Alloy steel fittings are commonly used in applications where high strength and reliability are critical, such as crane hooks, shackles, and lifting links.
[IMAGE: Examples of wire rope fittings made from carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel.]
Choosing the Right Material Based on the Application
The choice of material for wire rope fittings depends on the specific requirements of the application. Consider the following factors:
- Load: Select a material with sufficient strength to handle the load.
- Environment: Choose a material that is resistant to corrosion and other environmental factors.
- Temperature: Select a material that can withstand the operating temperature.
- Cost: Balance the cost of the material with its performance and lifespan.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the right material for your wire rope fittings and ensure safe and reliable operation.
Installation and Maintenance Best Practices
Proper Installation Techniques for Each Fitting Type
Proper installation is critical for ensuring the safe and reliable performance of wire rope fittings. The installation techniques vary depending on the type of fitting. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use the correct tools and equipment.
For example, when installing clip fittings, ensure the saddle is placed on the live side of the wire rope and that the nuts are tightened to the specified torque. When installing swage fittings, use the correct die size and apply the appropriate pressure.
Regular Inspection Procedures: Identifying Wear and Damage
Regular inspections are essential for identifying wear, damage, and corrosion in wire rope fittings. Inspections should be conducted before each use and at regular intervals, depending on the severity of the application.
What to Look For:
- Cracks: Check for cracks in the fitting body, especially around welds and stress points.
- Deformation: Look for any signs of deformation, such as bending or twisting.
- Wear: Check for wear on the bearing surfaces, such as the eyes of shackles and the grooves of sheaves.
- Corrosion: Look for signs of corrosion, such as rust or pitting.
- Loose or Missing Parts: Check for loose or missing nuts, bolts, and pins.
Any fitting that shows signs of wear, damage, or corrosion should be removed from service and replaced.
Lubrication and Cleaning Guidelines
Lubrication can help to reduce friction and wear in wire rope fittings, extending their lifespan. Use a lubricant that is compatible with the fitting material and the operating environment.
Cleaning can help to remove dirt, debris, and contaminants that can accelerate wear and corrosion. Use a mild detergent and water to clean the fittings, and then dry them thoroughly.
Replacement Schedules and End-of-Life Criteria
Wire rope fittings have a finite lifespan and should be replaced at regular intervals, depending on the severity of the application. The replacement schedule should be based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and the results of regular inspections.
End-of-Life Criteria:
- Cracks or Deformation: If the fitting has any cracks or deformation, it should be replaced immediately.
- Excessive Wear: If the fitting shows signs of excessive wear, it should be replaced.
- Severe Corrosion: If the fitting is severely corroded, it should be replaced.
- Exceeded Lifespan: If the fitting has exceeded its recommended lifespan, it should be replaced, even if it shows no signs of wear or damage.
Following proper replacement schedules and end-of-life criteria is essential for maintaining the safety and reliability of lifting operations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Selecting and Using Wire Rope Fittings
Mismatched Fittings and Wire Rope Sizes
One of the most common mistakes is using mismatched fittings and wire rope sizes. Always ensure that the fitting is the correct size for the wire rope being used. Using a fitting that is too small can lead to overloading and failure, while using a fitting that is too large can result in improper seating and reduced strength.
[IMAGE: An example of mismatched wire rope and fitting sizes.]
Incorrect Installation and Tightening
Incorrect installation and tightening can significantly reduce the strength and reliability of wire rope fittings. Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions and use the correct tools and equipment. Ensure that nuts and bolts are tightened to the specified torque and that all parts are properly seated and secured. We’ve seen numerous instances where neglecting this simple step led to costly accidents.
Neglecting Regular Inspections and Maintenance
Neglecting regular inspections and maintenance can allow wear, damage, and corrosion to go undetected, leading to unexpected failures. Regular inspections should be conducted before each use and at regular intervals, depending on the severity of the application. Proper lubrication and cleaning can also help to extend the lifespan of wire rope fittings.
Overlooking Environmental Factors
Overlooking environmental factors, such as temperature, corrosion, and abrasion, can lead to premature failure of wire rope fittings. Select materials and coatings that are appropriate for the operating environment. In harsh environments, consider using stainless steel or alloy steel fittings with protective coatings.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
OSHA Regulations for Lifting and Rigging
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has specific regulations for lifting and rigging equipment, including wire rope and fittings. These regulations are designed to protect workers from hazards associated with lifting operations.
Some key OSHA regulations include:
- 1926.251: Rigging equipment for material handling.
- 1926.1400: Cranes and derricks in construction.
- 1910.184: Slings.
Employers are responsible for ensuring that all lifting and rigging equipment complies with OSHA regulations and that workers are properly trained in their safe use.
ASME Standards for Wire Rope and Fittings
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) develops and publishes standards for wire rope and fittings. These standards provide detailed specifications for design, manufacturing, testing, and use.
Some key ASME standards include:
- ASME B30.9: Slings.
- ASME B30.26: Rigging Hardware.
Compliance with ASME standards is widely recognized as a best practice for ensuring the safety and reliability of lifting operations.
Other Relevant Industry Standards
In addition to OSHA regulations and ASME standards, other industry standards may be relevant to your specific application. These standards may be developed by organizations such as:
- American Petroleum Institute (API)
- American Institute of Steel Construction (AISC)
- National Fire Protection Association (NFPA)
It’s important to be aware of and comply with all relevant industry standards to ensure the safety and legality of your lifting operations.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Fitting Selection
Example 1: Construction Site Crane Lifting
Scenario: A construction site crane is used to lift heavy concrete beams.
Requirements:
- High Load Capacity
- Resistance to Abrasion
- Compliance with OSHA Regulations
Fitting Selection:
- Alloy Steel Shackles: Provide high strength and durability.
- Wire Rope Slings with Thimble Eyes: Protect the wire rope from wear and distortion.
- Regular Lay Wire Rope: Offers good resistance to crushing and abrasion.
Rationale: Alloy steel shackles offer the necessary strength for lifting heavy concrete beams, while wire rope slings with thimble eyes ensure the wire rope is protected from abrasion and kinking. The regular lay wire rope is selected for its resistance to crushing and abrasion, which are common on construction sites.
Example 2: Marine Application: Securing a Vessel
Scenario: A vessel needs to be securely moored in a saltwater environment.
Requirements:
- Corrosion Resistance
- High Strength
- Flexibility
Fitting Selection:
- Stainless Steel Shackles: Provide excellent corrosion resistance.
- Stainless Steel Turnbuckles: Allow for tension adjustment.
- Stainless Steel Wire Rope: Offers superior corrosion resistance in saltwater environments.
Rationale: Stainless steel is chosen for its excellent corrosion resistance in saltwater environments. Stainless steel shackles and turnbuckles provide the necessary strength and adjustability for securing the vessel.
Example 3: Industrial Manufacturing: Overhead Crane System
Scenario: An overhead crane system in a manufacturing plant is used to lift and move heavy machinery.
Requirements:
- High Strength
- Reliability
- Compliance with ASME Standards
Fitting Selection:
- Alloy Steel Lifting Links: Provide high strength and durability.
- Swage Fittings: Offer a strong and reliable termination.
- IWRC Wire Rope: Provides high strength and resistance to crushing.
Rationale: Alloy steel lifting links offer the necessary strength for lifting heavy machinery. Swage fittings provide a strong and reliable termination for the wire rope, while the IWRC wire rope ensures high strength and resistance to crushing, which are essential for overhead crane systems.
Advanced Considerations: Custom Fittings and Specialized Applications
Designing Custom Fittings for Unique Needs
In some cases, standard wire rope fittings may not be suitable for a particular application. In these situations, custom fittings may need to be designed and manufactured.
When designing custom fittings, consider the following factors:
- Load Requirements: Determine the maximum load that the fitting will need to carry.
- Environmental Conditions: Choose a material that is resistant to corrosion and other environmental factors.
- Space Constraints: Design the fitting to fit within the available space.
- Regulatory Standards: Ensure that the fitting complies with all relevant regulatory standards.
Working with a qualified engineer and manufacturer is essential for designing and producing custom fittings that meet your specific needs.
High-Performance Fittings for Extreme Environments
Extreme environments, such as those found in offshore oil and gas operations or high-altitude construction sites, may require the use of high-performance fittings. These fittings are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, pressures, and corrosive conditions.
Examples of high-performance fittings include:
- Cryogenic Fittings: Designed for use in extremely cold temperatures.
- High-Pressure Fittings: Designed for use in high-pressure applications.
- Corrosion-Resistant Fittings: Designed for use in highly corrosive environments.
Selecting the right high-performance fittings is crucial for ensuring the safety and reliability of operations in extreme environments.
Working with Manufacturers for Specialized Solutions
When dealing with complex or specialized applications, it is often beneficial to work directly with wire rope fitting manufacturers. Manufacturers can provide valuable expertise and guidance in selecting the right fittings for your specific needs.
Manufacturers can also provide custom design and manufacturing services, allowing you to create fittings that are tailored to your unique requirements. Building a strong relationship with a reputable manufacturer can help you ensure the safety and reliability of your lifting operations.
Troubleshooting Common Wire Rope Fitting Problems
Identifying Causes of Fitting Failure
Wire rope fitting failures can occur for a variety of reasons, including:
- Overloading: Exceeding the WLL of the fitting.
- Improper Installation: Incorrect installation techniques.
- Wear and Tear: Normal wear and tear over time.
- Corrosion: Exposure to corrosive environments.
- Fatigue: Repeated loading and unloading cycles.
- Manufacturing Defects: Defects in the fitting material or construction.
Identifying the cause of failure is essential for preventing future problems. Conduct a thorough investigation to determine the root cause of the failure and take corrective action.
Repairing Damaged Fittings (When Allowed)
In some cases, damaged wire rope fittings can be repaired. However, repair is only allowed if it is performed by a qualified technician and in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.
Never attempt to repair a fitting if:
- It has cracks or deformation.
- It has been overloaded.
- It is severely corroded.
In these cases, the fitting should be removed from service and replaced.
Preventing Future Problems Through Proper Practices
Preventing future problems requires a proactive approach to wire rope fitting selection, installation, maintenance, and inspection.
Key preventive measures include:
- Proper Selection: Choose the right fittings for the application.
- Correct Installation: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections to identify wear and damage.
- Proper Maintenance: Lubricate and clean fittings regularly.
- Operator Training: Train operators in the safe use of wire rope and fittings.
- Compliance with Standards: Comply with all relevant regulatory standards and industry best practices.
By implementing these preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of wire rope fitting failures and ensure the safety and reliability of your lifting operations.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Wire Rope Fitting for Safety and Efficiency
Selecting the right wire rope fitting is a multifaceted process that demands careful consideration of numerous factors, from understanding the basics of wire rope construction to evaluating environmental conditions and adhering to regulatory standards. By accurately assessing your lifting requirements, choosing appropriate materials, following proper installation and maintenance practices, and troubleshooting potential issues, you’ve equipped yourself to make informed decisions that ensure both safety and efficiency. We at SSTC are confident that the knowledge you’ve gained will significantly enhance your ability to manage lifting operations effectively.
FAQ Section
Q: What is the most important factor to consider when selecting a wire rope fitting?
A: The most important factor is the Working Load Limit (WLL) of the fitting, which must be sufficient to handle the maximum load, including dynamic loads and safety factors.
Q: How often should wire rope fittings be inspected?
A: Wire rope fittings should be inspected before each use and at regular intervals, depending on the severity of the application. A detailed inspection schedule should be established based on the manufacturer’s recommendations and industry best practices.
Q: Can damaged wire rope fittings be repaired?
A: In some cases, damaged wire rope fittings can be repaired by a qualified technician, but only if the damage is minor and the repair is performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Fittings with cracks, deformation, or severe corrosion should never be repaired and must be replaced.
Q: What is the difference between breaking strength and working load limit?
A: Breaking strength is the force required to cause a fitting to fail, while the Working Load Limit (WLL) is the maximum load that a fitting is designed to safely carry. The WLL is always lower than the breaking strength to provide a margin of safety.
Q: How do environmental conditions affect wire rope fittings?
A: Environmental conditions such as temperature, corrosion, and abrasion can significantly affect the performance and lifespan of wire rope fittings. Select materials and coatings that are appropriate for the operating environment.
Q: What are some common mistakes to avoid when using wire rope fittings?
A: Common mistakes include using mismatched fittings and wire rope sizes, incorrect installation and tightening, neglecting regular inspections and maintenance, and overlooking environmental factors.
Q: Where can I find more information about regulatory standards for wire rope fittings?
A: Information about regulatory standards can be found on the OSHA website and in ASME standards publications. You can also consult with industry experts and manufacturers for guidance on compliance.
Q: What are the benefits of using thimble eyes in wire rope slings?
A: Thimble eyes protect the wire rope from wear and distortion, increasing its lifespan and improving load distribution. They also enhance safety by preventing kinking and abrasion.
Q: How do I calculate dynamic loads for lifting operations?
A: Dynamic loads are forces generated by motion or sudden impacts. To calculate dynamic loads, consider factors such as shock loading, acceleration and deceleration, and wind loads. Apply appropriate safety factors to account for these dynamic loads.
Q: What are the different types of steel used for wire rope fittings, and when should each be used?
A: The common types of steel are carbon steel (cost-effective, general-purpose), stainless steel (corrosion-resistant, marine and chemical environments), and alloy steel (high-strength, heavy-duty applications). The choice depends on load requirements, environmental conditions, temperature, and cost.
Q: What is a wire rope sling and when is it used?
A: A wire rope sling is a lifting device made from wire rope with end terminations such as eyes or hooks. It is used for connecting a load to a lifting device, such as a crane or hoist, and is suitable for heavy loads and harsh environments where high strength and durability are required.
Q: Can you explain the concept of tensile strength in relation to wire rope fittings?
A: Tensile strength refers to the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before breaking. In the context of wire rope fittings, a higher tensile strength indicates that the fitting can endure greater pulling forces without failing, making it crucial for ensuring safety and reliability in lifting applications.
Q: What is the role of cable hardware in wire rope systems?
A: Cable hardware encompasses all the fittings and accessories used to connect, secure, and adjust wire rope in a system. This includes shackles, turnbuckles, eye bolts, clip fittings, and more. The quality and correct application of cable hardware are essential for maintaining the integrity and safety of the entire wire rope system.
Q: What are eye bolts and how are they used with wire rope?
A: Eye bolts are bolts with a looped head designed to attach a wire rope or other hardware to a structure. They are commonly used to create lifting points or anchor points where wire rope can be easily connected using shackles or other fittings. The load capacity and material of the eye bolt must be carefully selected to match the requirements of the application.
Q: What is a turnbuckle and how is it used to adjust tension in a wire rope system?
A: A turnbuckle is a device used to adjust the tension in wire rope assemblies. It consists of a body with threaded ends that accept eye bolts or hooks. By rotating the body, the distance between the ends can be increased or decreased, thereby adjusting the tension in the wire rope. This is particularly useful in applications where precise tensioning is required, such as in rigging and structural supports.
Q: How does a swage fitting compare to a clip fitting in terms of strength and reliability?
A: A swage fitting generally offers higher strength and reliability compared to a clip fitting. Swage fittings are permanently deformed onto the wire rope, creating a strong and secure connection that can achieve a high percentage of the wire rope‘s tensile strength. Clip fittings, while easier to install, rely on friction and clamping force, which can be less reliable and have a lower holding strength.
Q: What is a wedge socket and how does it ensure a secure wire rope termination?
A: A wedge socket provides a strong and reliable method for terminating wire rope, particularly in applications where frequent adjustments or replacements are required. The wire rope is inserted into the basket, looped around the wedge, and then secured by a pin. As the load is applied, the wedge tightens against the wire rope, creating a strong grip.
Q: How do you determine the appropriate size of a shackle for a given wire rope and load?
A: To determine the appropriate size of a shackle, you need to consider the diameter of the wire rope and the load capacity required for the lifting operation. The shackle’s